
ТОР 5 статей:
Методические подходы к анализу финансового состояния предприятия
Проблема периодизации русской литературы ХХ века. Краткая характеристика второй половины ХХ века
Характеристика шлифовальных кругов и ее маркировка
Служебные части речи. Предлог. Союз. Частицы
КАТЕГОРИИ:
- Археология
- Архитектура
- Астрономия
- Аудит
- Биология
- Ботаника
- Бухгалтерский учёт
- Войное дело
- Генетика
- География
- Геология
- Дизайн
- Искусство
- История
- Кино
- Кулинария
- Культура
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Металлургия
- Мифология
- Музыка
- Психология
- Религия
- Спорт
- Строительство
- Техника
- Транспорт
- Туризм
- Усадьба
- Физика
- Фотография
- Химия
- Экология
- Электричество
- Электроника
- Энергетика
Bolus versus Continuous Infusion
Patients who were assigned to intravenous boluses of furosemide every 12 hours were more likely to require a dose increase at 48 hours than were those assigned to continuous intravenous infusion (21% vs. 11%, P=0.01). There was no significant difference between these groups in the likelihood of a switch to oral diuretics at 48 hours (22% in the bolus group and 26% in the continuous-infusion group, P=0.44). The median total dose of loop diuretics received over the course of 72 hours (in intravenous furosemide equivalents) was 592 mg in the bolus group as compared with 480 mg in the continuous-infusion group (P=0.06) (for details, see Section 5 in the Supplementary Appendix).
There was no significant difference between the two treatment groups in the primary efficacy end point of patient-reported global assessment of symptoms (mean AUC, 4236±1440 with boluses and 4373±1404 with continuous infusion; P=0.47) (Figure 1 FIGURE 1 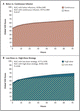 Patients' Global Assessment of Symptoms during the 72-Hour Study-Treatment Period.). There was also no significant between-group difference in the primary safety end point of the change in serum creatinine level from baseline to 72 hours (mean change in creatinine level, 0.05±0.3 mg per deciliter [4.4±26.5 μmol per liter] with boluses and 0.07±0.3 mg per deciliter [6.2±26.5 μmol per liter] with continuous infusion; P=0.45) (Figure 2 FIGURE 2
Patients' Global Assessment of Symptoms during the 72-Hour Study-Treatment Period.). There was also no significant between-group difference in the primary safety end point of the change in serum creatinine level from baseline to 72 hours (mean change in creatinine level, 0.05±0.3 mg per deciliter [4.4±26.5 μmol per liter] with boluses and 0.07±0.3 mg per deciliter [6.2±26.5 μmol per liter] with continuous infusion; P=0.45) (Figure 2 FIGURE 2  Mean Change in Serum Creatinine Level.). There was no evidence of an interaction between factorial groups (i.e., between the mode of administration and the dosing strategy) for either the primary efficacy end point (P=0.93) or the primary safety end point (P=0.70). There were also no significant between-group differences across a variety of secondary end points (Table 2 TABLE 2
Mean Change in Serum Creatinine Level.). There was no evidence of an interaction between factorial groups (i.e., between the mode of administration and the dosing strategy) for either the primary efficacy end point (P=0.93) or the primary safety end point (P=0.70). There were also no significant between-group differences across a variety of secondary end points (Table 2 TABLE 2  Secondary End Points for Each Treatment Comparison.). Serum creatinine and cystatin C levels were similar between the groups during the index hospitalization and at 60 days (see Section 6 in the Supplementary Appendix).
Secondary End Points for Each Treatment Comparison.). Serum creatinine and cystatin C levels were similar between the groups during the index hospitalization and at 60 days (see Section 6 in the Supplementary Appendix).
Не нашли, что искали? Воспользуйтесь поиском: